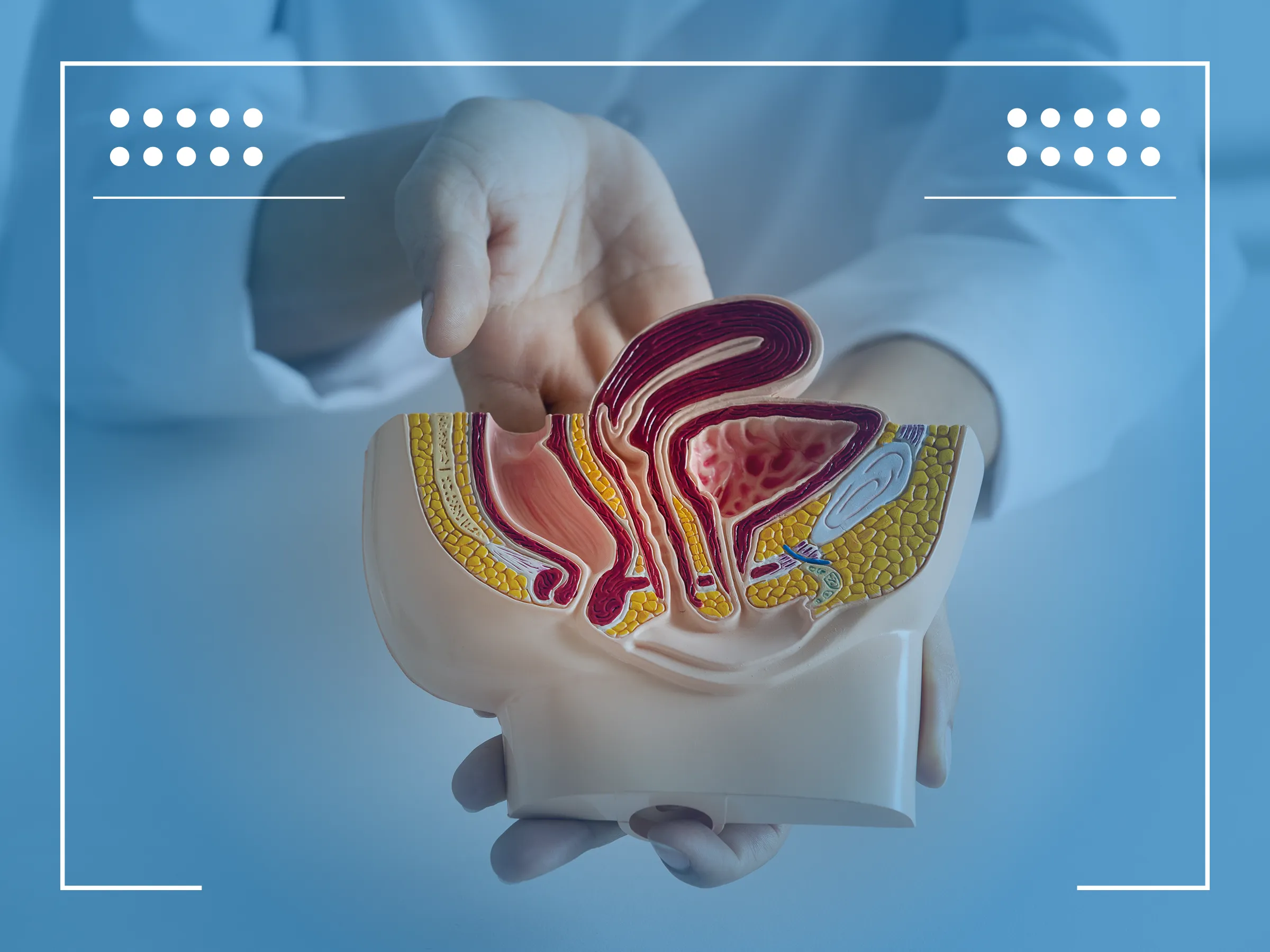
Urothelial carcinoma ICD-10, classified under the code C67, refers to a type of cancer that originates in the urothelium, the lining that forms the surface of the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra. This type of cancer is characterized by its location in the urinary system and its ability to affect various parts thereof.
Urothelial carcinoma ICD-10 coding not only categorizes the disease for medical records but also plays a crucial role in the management and treatment planning for affected individuals. Healthcare professionals use this code to identify the specific type of cancer, enabling them to choose the most effective treatment protocols. The classification under ICD-10 allows for a standardized approach to the diagnosis and treatment across different healthcare facilities worldwide, ensuring that patients receive consistent care. Additionally, this coding is essential for health insurance processing, medical research, and the development of new treatment strategies, emphasizing the importance of accurate and detailed medical coding in improving patient outcomes.
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common form of bladder cancer, and its diagnosis often leads to a detailed investigation of the urinary tract to assess the extent of the disease and to plan appropriate treatment. The ICD-10 coding system helps in the systematic recording and reporting of this cancer, facilitating research, treatment, and epidemiological studies.
ICD 10 Code for Urothelial Carcinoma
The ICD 10 code for urothelial carcinoma stands as a vital tool, enabling healthcare professionals to accurately document this specific type of cancer. Urothelial carcinoma represents a significant concern within oncology, primarily targeting the urinary system’s lining, notably the bladder wall. This contrasts with malignancies such as pancreatic cancer, which attacks the pancreas, or prostate cancer, focusing on the prostate gland.
The distinction between these cancers is critical, not only in terms of location, such as a bladder mass versus a renal cell carcinoma, but also in the approach to treatment and prognosis. For instance, a neuroendocrine tumor might require a different therapeutic strategy than urothelial carcinoma, despite both being classified under malignant neoplasms.
In the context of bladder-related diagnoses, ICD-10 bladder cancer codes are meticulously used to describe conditions ranging from a benign bladder mass to malignant tumors. For patients with a history of this disease, the history of bladder cancer ICD 10 code provides a concise way to communicate this critical information across medical platforms, ensuring continuity and accuracy in patient care.
Moreover, the bladder mass ICD 10 classification allows for a nuanced documentation of tumors, facilitating targeted treatment plans. This is especially pertinent for metastatic urothelial carcinoma ICD 10 cases, where the cancer has spread beyond its original location, necessitating a comprehensive approach to management.
It’s worth noting that the location of the tumor, such as the lateral wall of the bladder, can influence treatment decisions and outcomes. Accurate coding, therefore, not only supports effective patient management but also contributes to the broader understanding of urothelial carcinoma within the medical community.
In summary, the ICD-10 code for urothelial carcinoma and related classifications play a crucial role in the diagnosis, treatment, and research of bladder cancer. By offering a standardized language for healthcare providers, these codes ensure that patients receive personalized and effective care, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes.