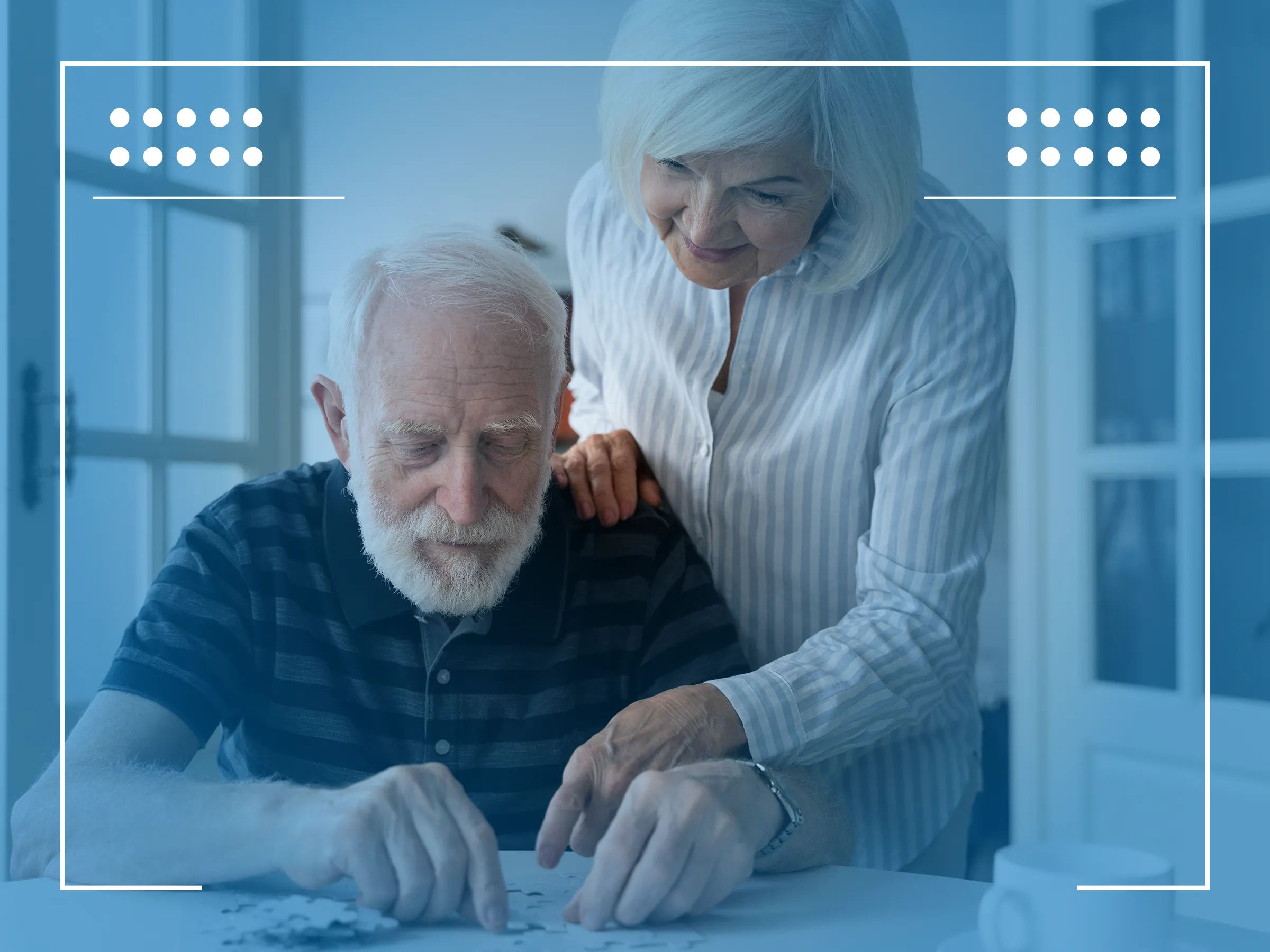
7 stages of Lewy body dementia begin with the early symptoms, which can be subtle and often mistaken for normal aging. Symptoms may include slight memory difficulties, mild confusion, and mood changes. As the condition is progressive, these early signs are crucial for early diagnosis and management. It is during these initial stages that interventions can be most effective, aiming to slow the progression and improve quality of life.
7 stages of Lewy body dementia continue to evolve as the disease progresses into more advanced stages. Here, symptoms become more pronounced and debilitating. Patients may experience significant memory loss, severe mood swings, and hallucinations. Physical symptoms such as tremors and muscle rigidity can also appear, resembling Parkinson’s disease. Each stage brings its own set of challenges, requiring adjustments in care strategies to handle the increasing needs of the patient.
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) does not have a universally recognized seven-stage progression like Alzheimer’s Disease, which is often described using such a framework. However, LBD can be conceptualized in terms of a progression through different stages of symptom severity, which can be useful for understanding how the disease typically evolves. Here’s a generalized overview of how symptoms can progress in LBD, categorized into broad stages:

Early Stage: Mild Symptoms
- Subtle memory problems, especially with retaining new information.
- Mild mood changes and depression.
- Slight motor difficulties, similar to early Parkinson’s disease symptoms, such as tremors or stiffness.
Developing Stage: Moderate Symptoms
- Worsening of motor symptoms, with increased risk of falls.
- More pronounced memory impairment, though some days might be better than others.
- Increased frequency and severity of hallucinations.
Middle Stage: Increased Dependency
- Further cognitive decline, leading to significant confusion and difficulty with logical thinking and planning.
- Greater difficulties with speech and communication.
- Need for assistance with daily activities and personal care.
Advanced Stage: Severe Symptoms
- Near-total dependence on caregivers for daily activities.
- Continued worsening of motor skills, possibly becoming wheelchair-bound or bedridden.
- Possible loss of verbal abilities.
What are the 7 Stages of Lewy Body Dementia?
Lewy body dementia is a complex, progressive disease characterized by the accumulation of Lewy bodies in brain cells. Understanding its progression can help caregivers and family members better support those affected.
How quickly does Lewy body progress?
The progression of Lewy body dementia can vary widely among individuals. For some, symptoms may worsen gradually over several years, while in others, they might experience more rapid declines. It is not uncommon for patients to have periods of stability followed by sudden worsening.
Is Lewy body the worst dementia?
While it’s challenging to categorize one type of dementia as the ‘worst,’ Lewy body dementia is particularly difficult to manage due to its complex symptoms, including cognitive decline, sleep disturbances, visual hallucinations, and Parkinsonian motor symptoms. Compared to other forms, such as frontotemporal dementia (FTD), its symptoms can be more unpredictable, significantly impacting quality of life.
Can Lewy body dementia get worse suddenly?
Yes, patients with dementia with Lewy bodies may experience sudden and dramatic fluctuations in cognitive abilities, alertness, and attention. These sudden changes can be distressing for both the patient and their caregivers, necessitating a flexible and patient approach to care.
What is the life expectancy for Lewy body dementia?
The life expectancy for someone with Lewy body disease can vary, but on average, individuals live 5 to 8 years after symptoms begin. The range, however, can be significantly broader, as much depends on the individual’s general health, age at diagnosis, and the severity of their symptoms.
In summary, dementia Lewy bodies pose a challenging journey for both the affected individuals and their families. It is important to seek early diagnosis and tailored care planning to manage the symptoms effectively. Whether dealing with frontal lobe dementia, FTD disease, or Lewy body dementia symptoms, understanding the specific needs and stages of each type can greatly aid in managing this complex condition.