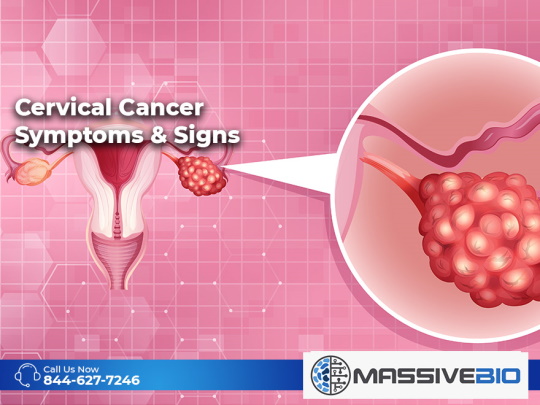
Cervical cancer symptoms and signs are difficult to detect in early stages early, and therefore, are usually noticed too late when the disease progresses insidiously. This is an indicator of how important regular cancer screenings are for women.
If cervical cancer symptoms and signs are detected early, it can prevent the devastating effects caused by cervical cancer. Cervical cancer differs from uterine cancer due to the region where it originates. Uterine cancer begins in the cells in the lining of the uterus called the uterine mucosa. The starting point of cervical cancer is the cervix, which connects the uterus and vagina.
What are Cervical Cancer Symptoms and Signs
Early-stage cervical cancer usually does not show any symptoms. Symptoms that occur in the late stages can be confused with pain during menstrual periods and urinary tract infections. The most common late stage symptoms include:
- Pain in the pelvis
- Unusual bleeding that occurs despite menopause
- Vaginal discharge with an unusual appearance or smell
- Longer than usual and heavier menstrual bleeding
- Need to urinate more often and urinary incontinence
- Burning and pain when urinating
- Bleeding and pain that occur outside of menstrual days
- Bleeding after intercourse, shower or pelvic exam
- Unexplained and persistent back pain
- Intense pain during sexual intercourse
Although some of these symptoms seem like the symptoms of other non-cancer diseases, it is important to take symptoms seriously and consult a specialist for early diagnosis. The sooner precancerous cells or cancer are detected and treated, the more likely the cancer will be prevented and cured.
Clinical Trial Search Tool
More than 15,000 clinical trials are currently recruiting patients of all cancer types and stages.
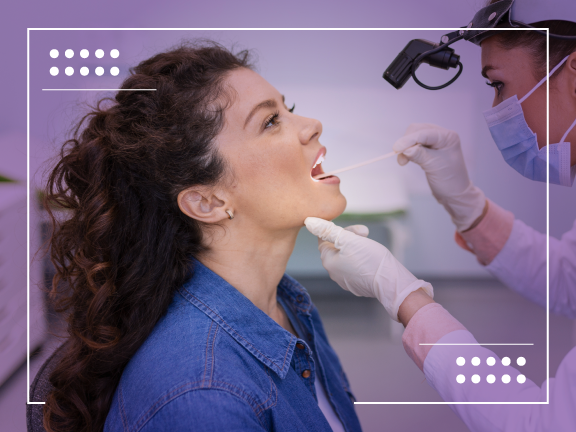
How Is Cervical Cancer Diagnosed?
The Pap Smear Test is used for the diagnosis of cervical cancer. This test is recommended from the age of 21 or 3 years after the first time experiencing sexual intercourse. Women are recommended to have a Pap Smear Test once a year to prevent cancer.
Approximately 15 days must have passed since the beginning of the last menstrual period for the test to be successful. In addition, sexual intercourse should be avoided 2 days before the test. It is important to clean the vagina carefully. If there is a vaginal infection, testing should not be done before treatment for this infection.
Cervical Cancer Treatment
- Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
- Immunotherapy applied simultaneously with other treatments
- Surgical removal of the tumor area
If the above treatments are not effective, clinical trials may be a good option for these patients. Patients at any stage of the disease can be included in clinical trials, if they meet the enrollment criteria. Clinical research with the development of new drugs, targeted therapies and immunotherapies may offer hope for advanced cervical cancer patients. If you want to be a part of a clinical trial and search for promising clinical trials near you, you can contact Massive Bio. Thousands of clinical trials are available for cancer patients and our artificial intelligence powered platform finds matching trials for you.










3 Comments
My doc says I have HPV and higher risk of cancer because of smoking. I am worried that I might have cancer. How can I avoid cervical cancer?
Hi Bianca, One of our Patient Relations Coordinators would be happy to listen to your case and provide support. We are available by live chat, email at support@massivebio.com, and by phone at 844-627-7246
It’s great to know that detecting cervical cancer earlier will help prevent the devastating effects it can cause you. In that case, one of the things I should undergo is an NDIS continence consultation when I feel like I am experiencing it. It’s important that I prevent severe illnesses when I get older for my own benefit. https://www.dreamcare121.com.au/continence-support