Ovarian Suppression
Ovarian suppression is a medical treatment primarily used in oncology to manage hormone-sensitive cancers. It involves reducing or stopping the production of hormones by the ovaries, which can significantly impact disease progression and recurrence.

Key Takeaways
- Ovarian suppression is a medical strategy to halt ovarian hormone production, often used in breast cancer treatment.
- It works by blocking signals to the ovaries or directly suppressing their function, reducing estrogen levels in the body.
- Benefits include slowing cancer growth and reducing recurrence rates in hormone-sensitive cancers.
- Common side effects are similar to menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes, bone density loss, and mood changes.
- The decision to undergo ovarian suppression is made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering individual health and cancer type.
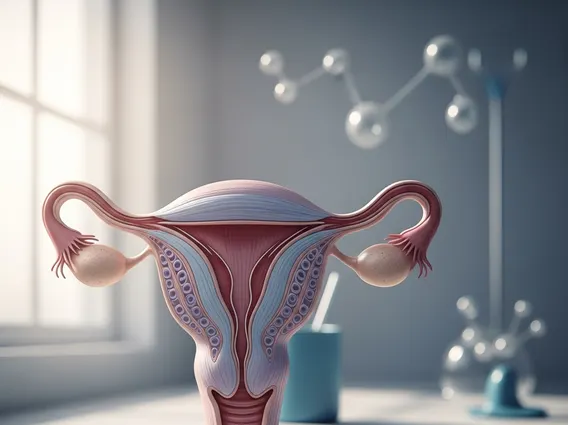
What is Ovarian Suppression?
Ovarian suppression refers to a medical intervention designed to reduce or completely stop the function of the ovaries, thereby decreasing the production of female hormones, primarily estrogen. This therapeutic approach is most commonly employed in the treatment of hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer, where estrogen can fuel cancer cell growth. By limiting the body’s estrogen supply, ovarian suppression aims to inhibit the proliferation of these cancer cells, improving patient outcomes.
How Ovarian Suppression Works and Its Benefits
Ovarian suppression works by various mechanisms to achieve its goal of reducing estrogen levels. One common method involves the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, such as goserelin or leuprolide. These medications initially stimulate, then desensitize, the pituitary gland’s receptors, leading to a significant decrease in the production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). As a result, the ovaries receive fewer signals to produce estrogen, effectively putting them into a temporary, reversible menopause-like state. Surgical removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy) or radiation therapy to the ovaries are permanent methods of ovarian suppression.
The benefits of ovarian suppression therapy are particularly significant for premenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer. Clinical studies, such as those cited by the National Cancer Institute, have shown that combining ovarian suppression with tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors can significantly improve disease-free survival and overall survival rates compared to tamoxifen alone in certain patient populations. For instance, a meta-analysis published in The Lancet Oncology found that adding ovarian suppression to endocrine therapy reduced the risk of recurrence by approximately 15% in premenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive early breast cancer. This therapy helps to create a less hospitable environment for hormone-sensitive cancer cells, thereby reducing the risk of cancer recurrence and improving long-term prognosis.
Side Effects of Ovarian Suppression Therapy
While highly effective, ovarian suppression side effects can be considerable, as they essentially induce a menopausal state in premenopausal women. These side effects are largely due to the sudden and significant drop in estrogen levels. Patients may experience a range of symptoms that can impact their quality of life.
Common side effects include:
- Hot flashes and night sweats: These are among the most frequently reported symptoms, often described as sudden feelings of intense heat.
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort: Reduced estrogen can lead to thinning and drying of vaginal tissues, causing pain during intercourse.
- Mood changes and depression: Hormonal fluctuations can affect emotional well-being, leading to irritability, anxiety, or depressive symptoms.
- Loss of bone mineral density: Long-term estrogen deprivation can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Regular monitoring and bone-strengthening strategies are often recommended.
- Weight gain and metabolic changes: Some women may experience changes in metabolism, leading to weight gain.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness is another common complaint.
It is crucial for patients undergoing ovarian suppression to discuss these potential side effects with their healthcare team. Management strategies, including lifestyle adjustments, supportive medications, and bone health interventions, can help mitigate these symptoms and improve overall comfort during treatment.