Hemilaryngectomy
Hemilaryngectomy is a specialized surgical procedure primarily used in the treatment of laryngeal cancer. This article provides an overview of what the procedure entails, its surgical process, and what patients can expect regarding recovery and potential side effects.
Key Takeaways
- Hemilaryngectomy is a surgical procedure to remove part of the larynx, typically to treat early-stage laryngeal cancer.
- The goal is to remove cancerous tissue while preserving as much voice and swallowing function as possible.
- The surgical process involves precise removal of affected vocal cord(s) and surrounding cartilage.
- Recovery includes managing pain, speech therapy, and adapting to potential changes in voice and swallowing.
- Potential side effects include changes in voice quality, difficulty swallowing, and temporary breathing issues.
What is Hemilaryngectomy?
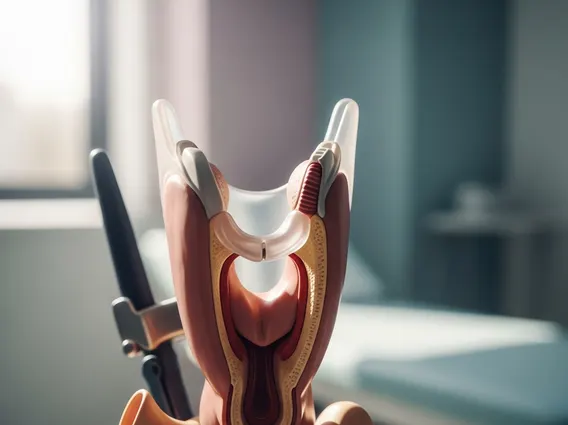
Hemilaryngectomy is a surgical procedure involving the partial removal of the larynx, also known as the voice box. This operation is primarily performed to treat early-stage laryngeal cancer, specifically when the tumor is confined to one vocal cord or a limited area of the larynx. The main objective is to eradicate cancerous tissue while preserving as much of the patient’s voice and swallowing function as possible. Unlike a total laryngectomy, which removes the entire voice box, a hemilaryngectomy aims to maintain significant structural integrity, allowing for better functional outcomes post-surgery. The decision depends on various factors, including tumor size and location, patient health, and impact on quality of life.
The Hemilaryngectomy Surgical Process
The hemilaryngectomy procedure details involve a meticulous surgical approach designed to remove the cancerous portion of the larynx. Before surgery, patients undergo thorough evaluations, including imaging scans and biopsies, to precisely map the tumor’s extent. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, with the surgeon making an incision in the neck to access the larynx. Depending on the specific type of hemilaryngectomy, the surgeon removes one vocal cord, part of the thyroid cartilage, and any other affected laryngeal structures. The goal is to achieve clear margins, meaning all cancerous cells are removed, while leaving healthy tissue intact.
Key steps often include:
- Incision: A cut is made in the neck to expose the larynx.
- Tumor Resection: The cancerous section of the larynx, including part of the vocal cord and associated cartilage, is carefully removed.
- Reconstruction (if necessary): Remaining tissues may be reshaped or grafted to help restore laryngeal function.
- Tracheostomy (temporary): A temporary breathing tube may be inserted into the windpipe to secure the airway during initial recovery, usually removed once the airway is stable.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures.
The surgery typically lasts several hours, and patients are closely monitored post-surgery.
Recovery and Potential Side Effects After Hemilaryngectomy
Following surgery, hemilaryngectomy recovery information is crucial for patients to understand the healing process. Immediately after the procedure, pain and discomfort are managed with medication. A temporary tracheostomy tube, if placed, will require care and is typically removed within days or weeks as swelling subsides. Swallowing may be difficult initially, potentially requiring a feeding tube for a short period. Speech therapy is vital, helping patients adapt to voice changes and improve swallowing. The voice will likely be hoarse or breathy, its quality depending on the extent of tissue removal and remaining structures’ function.
Understanding hemilaryngectomy side effects explained is important for managing expectations. Common side effects include:
- Voice Changes: Hoarseness, breathiness, or a weaker voice are almost universal due to vocal cord alteration.
- Swallowing Difficulties (Dysphagia): Trouble swallowing, leading to coughing or choking, especially with liquids. This often improves with therapy.
- Breathing Issues: Some patients might experience shortness of breath or noisy breathing due to airway changes.
- Neck Pain and Stiffness: Incision site pain and muscle stiffness are common initially.
- Scarring: A visible scar on the neck is inevitable.
Most patients require a hospital stay of several days to a week. Full recovery can take several weeks to months, involving work with speech-language pathologists and other healthcare professionals. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing and check for cancer recurrence.
