Jaw cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the jawbone or tissues around the jaw. It often originates from cells in the jaw or oral cavity. In its early stages it might not present noticeable symptoms. However, as it progresses, signs like swelling, pain, or lesions inside the mouth can become more evident. Making early detection critical for a more successful treatment outcome.
Jaw cancer can pose serious health risks if not treated promptly, as it may spread to surrounding tissues and other parts of the body. The treatment typically involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, depending on the stage and location of the cancer. In some cases, reconstructive surgery may be necessary to restore function and appearance after the tumor is removed. Maintaining oral health during the treatment process is crucial, as jaw cancer can affect eating, speaking, and overall quality of life. Regular dental check-ups, as well as close monitoring by a healthcare professional, are essential for early diagnosis and managing potential side effects of treatment.
Cancer of the jaw can be classified into different types depending on the origin of the cancerous cells. Understanding the type and stage of cancer is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach. Some common factors associated with cancer of the jaw include:
- Type of cancer: Jaw cancer can stem from various sources, such as squamous cell carcinoma, which affects the lining of the mouth, or osteosarcoma, which originates in the bone itself.
- Risk factors: Tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and a history of oral infections like HPV can increase the risk of developing jaw cancer.
- Symptoms: In addition to swelling and pain, other symptoms may include difficulty chewing, loose teeth, or numbness in the jaw area.
Early intervention is key. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific condition, including the location and spread of the tumor.
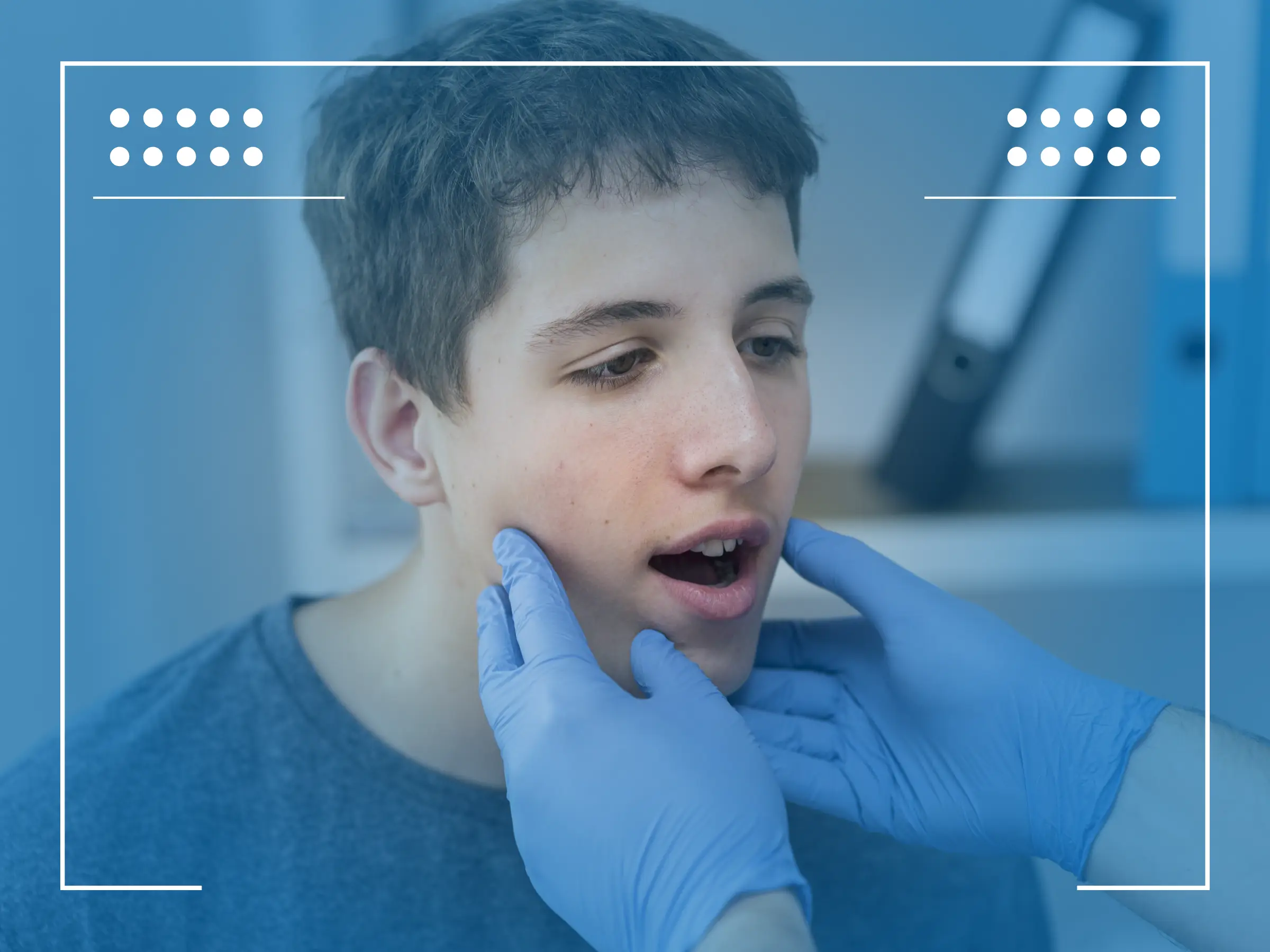
Jaw Cancer Symptoms
Jaw cancer can present a variety of symptoms, many of which may be subtle in the early stages. One of the most common signs of jaw cancer is persistent pain or discomfort in the jaw area. Other symptoms may include swelling, sores inside the mouth that don’t heal, or unusual lumps. Early detection is crucial as jaw cancer can spread quickly, especially to nearby areas like the tongue and other parts of the mouth.
The development of jaw cancer can be influenced by various causes, such as genetic factors, exposure to harmful substances, or a previous medical condition like a benign cyst turning malignant. Individuals of any age can develop jaw cancer, but older adults may be at higher risk. If there are persistent signs, an X-ray is often recommended by healthcare providers to detect abnormalities in the bone structure of the jaw.
Common symptoms of jaw cancer:
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Loose teeth or tooth pain
- Swelling or lumps in the jaw
- Numbness in the mouth or jaw area
Treatment options vary based on the stage and severity of the cancer. Cancer treatment for jaw cancer often involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. In cases where the tumor is extensive, reconstructive surgery may be needed to restore function.
Understanding the early signs of jaw cancer and seeking prompt medical advice can significantly improve the outcomes of the treatment process.