Female Colonoscopy Procedure: What Women Need to Know About Prep, Position, and Timing
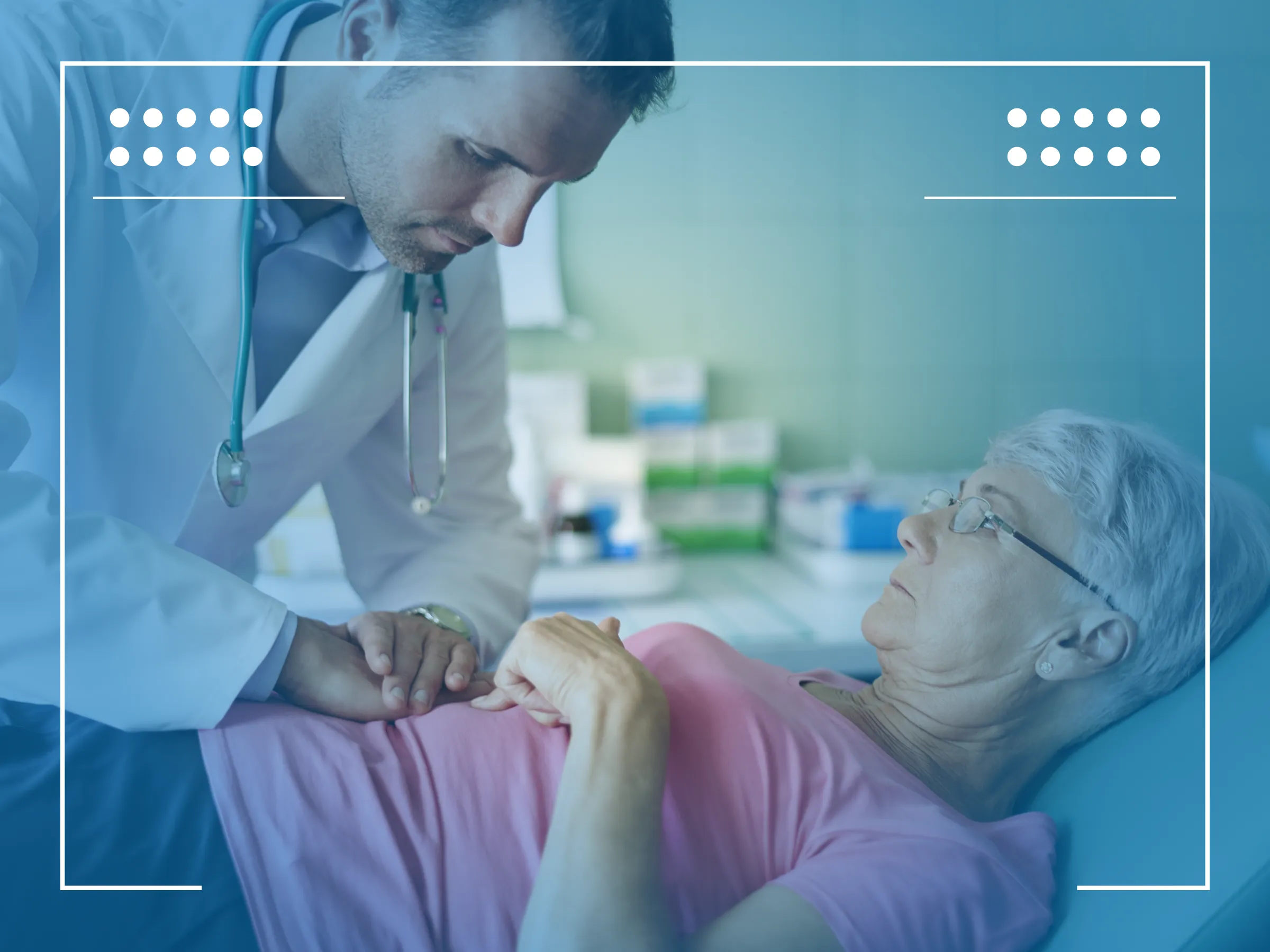
Understanding the details of the female colonoscopy procedure is essential for reducing anxiety and ensuring the process runs smoothly. From preparation to positioning and recovery, each step plays a role in the success of the examination. The prep involves dietary changes and laxatives to clear the bowel, usually starting the day before the procedure. Patients are often advised to follow a clear liquid diet and avoid colored drinks.
The female colonoscopy procedure position typically involves lying on the left side with knees drawn toward the chest. This allows for easier navigation of the colonoscope and more accurate visuals of the colon lining. The entire experience—from prep to post-procedure discussion—is streamlined for efficiency and comfort.
Knowing how long a female colonoscopy takes, and what to expect, empowers women to plan accordingly. Most procedures take between 30 and 60 minutes, with recovery time included. For women over 45, colonoscopy for women is not just a diagnostic tool—it’s a proactive health measure.
Female Colonoscopy Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide
Many women are unfamiliar with what happens during a female colonoscopy, which can increase apprehension. The procedure begins after sedation is administered. A doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube called a colonoscope into the rectum. This device has a small camera that allows the physician to inspect the colon lining for abnormalities like polyps or signs of inflammation.
If anything unusual is found, such as polyps, they can often be removed during the same session. This not only eliminates the need for a second procedure but also serves a preventive purpose. As a women’s colonoscopy is typically a low-risk outpatient procedure, most patients return home the same day.
This step-by-step overview helps demystify the process and highlights the preventive power of routine screenings. With increased awareness and timely screenings, many cases of colorectal cancer can be detected early or even prevented entirely.
Female Colonoscopy Procedure Position
The female colonoscopy procedure position plays a critical role in ensuring both patient comfort and procedural accuracy. The standard position is the left lateral decubitus, where the woman lies on her left side with knees slightly bent. This position offers optimal alignment for the colonoscope and facilitates smoother navigation through the sigmoid colon and beyond.
While this is the typical setup, adjustments may be made based on patient anatomy or prior surgical history. Some women with mobility issues or discomfort in this position may be guided into a modified posture.
Proper positioning helps reduce discomfort and improves the visibility of the colon lining, enhancing the likelihood of detecting any abnormalities. If you’re unsure about what to expect, consult your physician ahead of time. They will explain how the position contributes to a successful female colonoscopy experience.
How Female Colonoscopy Helps Prevent Colorectal Cancer
Female colonoscopy is a critical preventive tool in the fight against colorectal cancer. By enabling early detection of polyps and other irregularities, it helps catch potential cancerous growths before they become dangerous. Many women are unaware that polyps can be removed during a female colonoscopy, preventing them from developing into malignancies.
Routine screening is especially crucial for women over 45 or those with a family history of colorectal disease. With early intervention, treatment outcomes are significantly improved, and many serious complications can be avoided.
Additionally, colonoscopy for women often includes a biopsy if suspicious tissue is found. This enhances diagnostic accuracy and enables timely treatment. When scheduled at recommended intervals, women’s colonoscopies are one of the most effective ways to protect long-term gastrointestinal health.
Is a female colonoscopy painful?
No, most women experience little to no pain during the procedure due to sedation. Some may feel mild cramping or bloating afterward.
How long does a female colonoscopy take from start to finish?
Including prep, sedation, and recovery, the entire process typically takes 2 to 3 hours, with the colonoscopy itself lasting 30 to 60 minutes.
What is the proper position for a female colonoscopy procedure?
The standard position is lying on the left side with knees bent—known as the left lateral decubitus position.
At what age should a woman get her first colonoscopy?
Women should generally begin screenings at age 45. Earlier screenings may be necessary based on family or personal health history.
What should I eat before a female colonoscopy?
Stick to a clear liquid diet the day before your procedure—water, clear broth, and pulp-free juices are best. Avoid red or purple drinks.
Can polyps be removed during a female colonoscopy?
Yes, most small and medium polyps can be removed during the procedure, preventing them from turning into cancer.
How often should women have a colonoscopy?
If results are normal, every 10 years is standard. However, women with risk factors may need screenings more frequently.