English
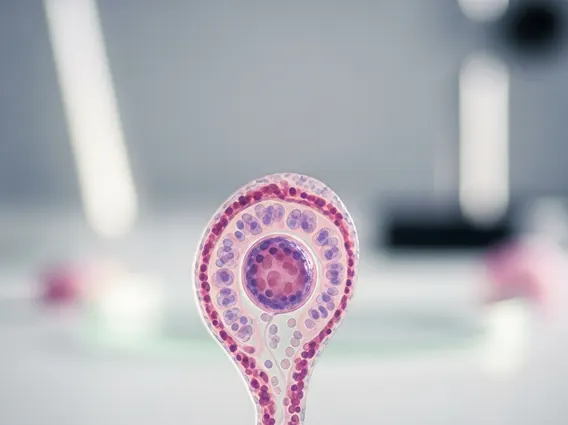
Ovarian germ cell tumors are a rare and diverse group of neoplasms originating from the primitive germ cells of the ovary. Understanding these tumors is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Key Takeaways
- Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor refers to rare ovarian cancers arising from germ cells.
- They primarily affect adolescents and young women, often presenting as a mass.
- Symptoms can include abdominal pain, swelling, and menstrual irregularities.
- Diagnosis involves imaging, blood tests for tumor markers, and tissue biopsy.
- Prognosis is generally favorable, especially with early detection and appropriate treatment.
What is Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor?
Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor refers to a heterogeneous group of cancers that develop from the primitive germ cells within the ovary. These cells are responsible for producing eggs and are typically found in the ovaries. While ovarian cancer is more commonly associated with epithelial tumors, these germ cell tumors represent a distinct and less common category, accounting for approximately 2-5% of all ovarian malignancies, according to the American Cancer Society. They predominantly affect adolescents and young women, often presenting as a mass. Unlike epithelial ovarian cancers, which are more common in older women, what are ovarian germ cell tumors are often highly curable, even when diagnosed at advanced stages.
Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor: Symptoms and Causes
Recognizing the ovarian germ cell tumor symptoms is vital for early detection. The signs and symptoms can vary depending on the tumor’s size, type, and whether it has spread. Common symptoms often include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, which may be persistent or intermittent.
- A palpable mass or swelling in the abdomen.
- Changes in menstrual patterns, such as irregular periods or amenorrhea.
- Nausea, vomiting, or a feeling of fullness after eating small amounts.
- Unexplained weight loss or gain.
- In some cases, hormonal activity of the tumor can lead to precocious puberty or virilization.
The exact ovarian germ cell tumor causes are not fully understood, but they are believed to arise from errors in the development of germ cells during embryonic development. Unlike many other cancers, there are no strong links to lifestyle factors or environmental exposures. Genetic factors may play a role in a small percentage of cases, but most occurrences are sporadic. Conditions like gonadal dysgenesis (abnormal development of the gonads) are known risk factors for certain types of germ cell tumors, particularly dysgerminomas, but these are rare.
Diagnosing Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor and Understanding Prognosis
The diagnosis of ovarian germ cell tumor typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Initial assessment often includes a physical examination, focusing on the abdomen and pelvis. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are crucial for identifying the tumor’s size, location, and potential spread. Blood tests are also essential, particularly for tumor markers like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), which can be elevated in specific types of germ cell tumors. A definitive diagnosis is usually made through a biopsy, often obtained during surgery, where tissue is examined under a microscope by a pathologist.
The prognosis for ovarian germ cell tumor is generally favorable, especially when compared to other types of ovarian cancer. The overall survival rates are high, often exceeding 90% for many types, even in advanced stages, due to their sensitivity to chemotherapy. Factors influencing prognosis include the specific type of germ cell tumor, the stage at diagnosis, and the patient’s response to treatment. Early detection significantly improves outcomes. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the tumor and affected ovary, often followed by chemotherapy, depending on the tumor type and stage. Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor for recurrence.