Abdominal
The term abdominal refers to the region of the body located between the chest and the pelvis, encompassing a vital cavity that houses numerous essential organs. Understanding this complex area is crucial for diagnosing and treating a wide range of medical conditions.
Key Takeaways
- The abdominal region is a critical part of the body, containing digestive, excretory, and reproductive organs.
- Abdominal pain and discomfort can stem from various causes, ranging from mild digestive issues to serious underlying conditions.
- Understanding the specific location and characteristics of abdominal symptoms can help identify potential causes.
- Common abdominal diseases include conditions affecting the digestive tract, liver, kidneys, and other organs within the cavity.
- Prompt medical evaluation is important for persistent or severe abdominal symptoms to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What is Abdominal: Definition and Anatomy
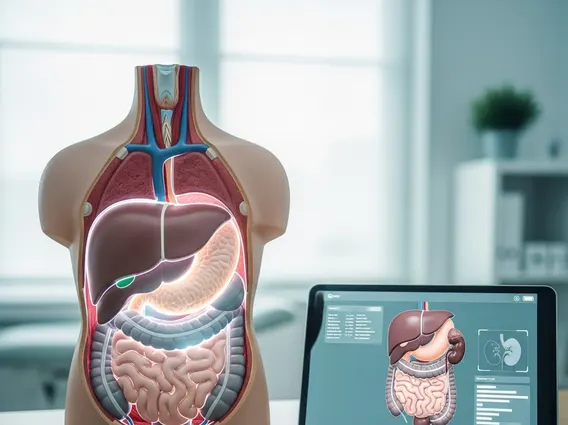
Abdominal refers to the abdomen, which is the part of the trunk located between the diaphragm and the pelvis. This region is enclosed by the abdominal wall, consisting of muscles, fascia, and skin, and it protects the abdominal cavity. The abdominal cavity is the largest body cavity and contains a vast array of organs vital for digestion, excretion, and reproduction.
The abdominal anatomy explained involves several key structures and regions. It is often divided into four quadrants or nine regions to help localize symptoms and findings. Major organs within this area include the stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands. The peritoneum, a serous membrane, lines the abdominal cavity and covers many of these organs, facilitating their movement and providing support.
Causes of Abdominal Pain and Discomfort
Abdominal pain and discomfort are common complaints that can arise from a multitude of sources, ranging from benign to severe. The abdominal pain causes can originate from any of the organs within the abdominal cavity or even from structures outside it, such as the chest or pelvis, due to referred pain. Common causes often relate to the digestive system, including indigestion, gas, constipation, or gastroenteritis.
What is Abdominal Discomfort?
Abdominal discomfort refers to a general feeling of unease, fullness, bloating, or mild pain in the abdominal area that is not severe enough to be classified as acute pain. It can be a vague sensation that is difficult to pinpoint to a specific location or organ. This discomfort often arises from functional issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), dietary intolerances, stress, or minor infections. While often transient, persistent abdominal discomfort warrants medical attention to rule out underlying conditions.
Other significant causes of abdominal pain include inflammatory conditions such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, or pancreatitis. Issues with the gallbladder, like gallstones, or kidney stones can also lead to intense pain. Vascular problems, such as mesenteric ischemia, or gynecological conditions in women, can also manifest as abdominal pain. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), abdominal pain is one of the most frequent reasons for emergency department visits in the United States.
Common Abdominal Diseases and Conditions
The abdomen is susceptible to a wide array of diseases and conditions given the number of organs it houses. Understanding the types of abdominal diseases is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. These conditions can affect any part of the digestive tract, liver, pancreas, kidneys, or other abdominal structures. Here are some common examples:
- Gastroenteritis: Inflammation of the stomach and intestines, often caused by viral or bacterial infections, leading to nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic functional disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and altered bowel habits (constipation, diarrhea, or both) without any visible signs of damage or disease in the digestive tract.
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix, a small, finger-shaped pouch projecting from the large intestine, typically causing sharp pain in the lower right abdomen.
- Gallstones: Hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in the gallbladder, leading to sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation or infection of small pouches (diverticula) that can form in the lining of the digestive system, particularly the colon.
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys, causing severe pain as they pass through the urinary tract.
Many abdominal diseases require careful diagnosis through imaging, blood tests, and sometimes endoscopy or colonoscopy. Early detection and appropriate medical management are key to preventing complications and improving patient outcomes.
Note: Information on alternative or complementary therapies is for supportive purposes only and does not replace professional medical treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
