AI Eşleştirme Sistemi
INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE
Clinical research teams manually screen patients for cancer trials, a process that can take ~25 minutes per single trial using highly specialized resources, restricting trial options available to patient, and negatively impacting enrollment rates.
Precision Cancer Consortium, including seven of the top 20 pharmaceutical companies, collaborated with Massive Bio to explore an innovative and efficient multi-trial matching method.
This initiative focused on shifting towards a multi-trial prescreening approach, incorporating NGS testing results, and using artificial intelligence to enhance accuracy and efficiency of trial matching, particularly for targeted therapies.
METHODS
AI-Enabled System: Massive Bio developed a state-of-the-art AI system that utilizes computer vision and natural language processing to extract 180 structured clinical parameters from medical records. This system also features an AI recommendation algorithm for matching patients to digitized inclusion/exclusion (I/E) criteria from over 14,000 actively recruiting interventional cancer trials.
Data Analysis and Algorithm Development: The study analyzed a sample of 5,707 cancer patients from the Massive Bio Synergy AI real-world database, focusing on tumor types relevant to 23 selected trials. A decision-tree algorithm was developed for retrospective matching. Results were compared to the theoretical matching rate based on specific criteria including tumor type, biomarker prevalence, disease extent at diagnosis, and prior treatment history.
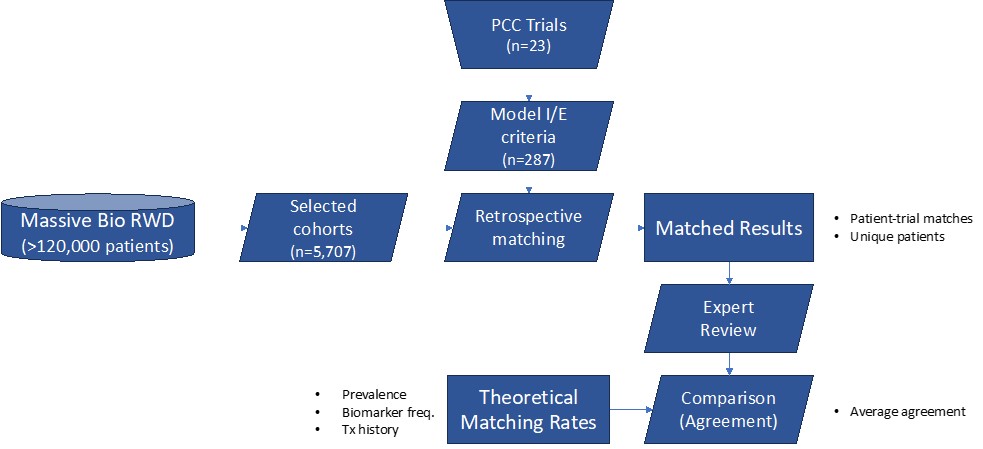
RESULTS
Records of 5,707 unique patient were selected, of which only 1,557 (27%) had NGS testing results available.
690 unique patients were matched to at least one trial. The total number of matching pairs (patient-trial) was 1,254 resulting in a 1.82-fold increase as a result of multi-trial matching.
In a simulated scenario, where 100% of patients were assumed to have NGS testing results, a total number of 2,635 matching patient-trial pairs were found. This implied a potential 2.1-fold increase from NGS testing.
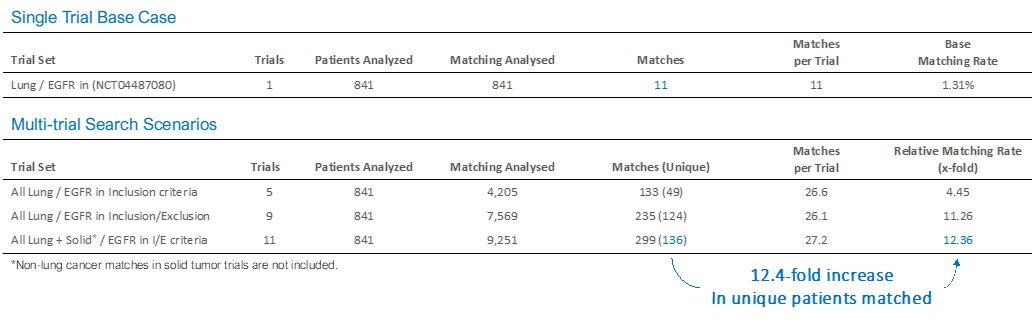
In a multi-trial case study, specific for lung cancer trials targeting wild-type or mutated EGFR gene, multi-trial matching to 11 trials resulted in 12.4-fold increase in unique patients compared to a single trial.
Compared to the theoretical matching rate, Massive Bio’s matching rate was significantly higher 50% of trials, and equivalent in 30%.
The total savings in effort was estimated to be 19,500 hours (99.9%).
Multi-trial matching and impact of genomic testing in multi-trial matching
| Sponsor | Trial | Tumor Types | Patients Analyzed | Had NGS Results | Exact Matches | Partial Matches | No-Matches: Fails NGS | Partial Matches: Missing only NGS | Partial Matches: Other than NGS | Potential Exact Matches Assuming 100% NGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ | NCT03997123 | Breast | 781 | 190 | 16 | 3 | 0 | (0%) | 3 (100%) | 16 (2.05%) |
| AZ | NCT04305496 | Breast | 781 | 190 | 54 | 0 (0%) | 8 (100%) | 8 | 0 | 54 (6.91% |
| Bayer | NCT03188965 | Lymphoma, Prostate, Breast, Colon, Rectal, Ovarian, Endometrial, Cervical | 2637 | 678 | 86 | 406 (72%) | 9 (2% | 564 | 305 | 182 (6.92%) |
| Bayer | NCT02576431 | Solid Tumors | 4939 | 1487 | 0 | 852 | 541 | 759 (89%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Bayer | NCT04147819 | Solid Tumors | 4939 | 1487 | 29 | 9 | 0 | 0 (0%) | 9 (100%) | 29 (0.59%) |
| Bayer | NCT05099172 | Lung | 841 | 260 | 47 | 194 | 175 | 139 (72%) | 5 (3%) | 79 (9.37%) |
| GSK | NCT02064387 | Multiple Myeloma | 223 | 9 | 91 | 23 | 0 | 0 (0%) | 23 (100%) | 91 (40.81%) |
| GSK | NCT02655016 | Ovarian | 163 | 77 | 9 | 27 | 18 | 27 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 18 (11.04%) |
| GSK | NCT02715284 | Solid Tumors | 4939 | 1487 | 587 | 1647 | 340 | 1291 (78%) | 80 (5%) | 1442 (29.20%) |
| GSK | NCT05723562 | Rectal | 81 | 45 | 0 | 11 | 3 | 5 (45%) | 1 (9%) | 1 (1.53%) |
| JNJ | NCT05601973 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 9 | 3 | 10 | 1 (33%) | 2 (67%) | 9 (1.13%) |
| JNJ | NCT04538664 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 6 | 213 | 206 | 125 (59%) | 2 (1%) | 11 (1.27%) |
| JNJ | NCT03390504 | Urothelial | 49 | 9 | 2 | 12 | 6 | 11 (92%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (9.69%) |
| JNJ | NCT04487080 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 11 | 81 | 107 | 69 (85%) | 0 (0%) | 17 (2.07%) |
| JNJ | NCT04988295 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 24 | 11 | 12 | 1 (9%) | 8 (73%) | 25 (2.94%) |
| Lilly | NCT05307705 | Solid Tumors | 4939 | 1487 | 73 | 1733 | 700 | 1253 (72%) | 24 (1%) | 226 (4.57%) |
| Lilly | NCT05614739 | Solid Tumors | 4939 | 1487 | 29 | 1671 | 882 | 1280 (77%) | 15 (1%) | 90 (1.82%) |
| Lilly | NCT04956640 | Solid Tumors | 4939 | 1487 | 65 | 1557 | 1009 | 1180 (76%) | 13 (1%) | 150 (3.03%) |
| Lilly | NCT04194944 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 0 | 181 | 220 | 153 (85%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Novartis | NCT05132075 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 17 | 100 | 107 | 90 (90%) | 1 (1%) | 30 (3.56%) |
| Novartis | NCT05445843 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 79 | 117 | 83 | 71 (61%) | 17 (15%) | 117 (13.92%) |
| Novartis | NCT05791097 | Lung | 841 | 293 | 6 | 19 | 8 | 9 (47%) | 3 (16%) | 11 (1.28%) |
| Roche | NCT02091141 | Solid Tumors | 4939 | 1487 | 14 | 1395 | 822 | 950 (68%) | 2 (0%) | 32 (0.65%) |
| Unique: | 5,707 | 1,557 | 690 | 2,216(100%) | 1,123 | 1.729(78%) | 172(8%) | estimated 1,290 | ||
| Total: | 46,857 | 14,211 | 1,254 | 10,431(100%) | 5,554 | 7,820(75%) | 225(2%) | 2,635 | ||
| 2.1-fold increase in patient-trial matches assuming 100% NGS testing | ||||||||||
CONCLUSION
The combination of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) with Artificial Intelligence (AI) in a multi-trial matching approach resulted in a nearly 2-fold increase potential patient eligibility for trials for all tumor types and 12-fold increase in a single focused tumor profile, along with a dramatic reduction in manual effort.

© 2024 Massive Bio. All rights reserved




